Key Takeaways
- GIS technology integrates spatial data with analytical tools to support informed decision-making across multiple industries.
- Applications of GIS range from urban planning and environmental management to healthcare and public safety.
- Recent advancements in GIS include the incorporation of artificial intelligence and real-time data processing.
Table of Contents
- Urban Planning and Development
- Environmental Management
- Healthcare and Public Health
- Transportation and Logistics
- Public Safety and Emergency Response
- Agriculture and Natural Resources
- Advancements in GIS Technology
- Conclusion
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are transforming how organizations analyze, interpret, and leverage spatial information for effective decision-making. From city planners to healthcare professionals, a deep understanding of what is GIS mapping empowers industries to unlock efficiencies, conserve resources, and solve complex challenges that require geographical insights. As GIS matures and integrates new technologies, its influence continues to expand across almost every sector.
GIS technology integrates multiple datasets into digital maps, enabling powerful visualization and analysis for smarter decision-making. It supports governments in sustainable development, businesses in market intelligence, and communities in improving access to services. Its versatility enhances collaboration, operational efficiency, and predictive capabilities across logistics, public health, and urban planning. As digital transformation accelerates, GIS remains vital for addressing modern environmental and societal challenges, making it an essential tool for building agile, resilient organizations.
Urban Planning and Development
Urban planners turn to GIS to anticipate and manage the rapid growth and complexity of city environments. By simulating land use, infrastructure needs, and transportation networks, GIS allows planners to establish smart zoning regulations, evaluate the environmental impacts of development, and map out sustainable future growth. According to Architect Magazine, GIS has become a vital tool in architecture, urban design, and planning, helping professionals visualize and analyze data to make more informed decisions.
Through 3D urban modeling and dynamic scenario analysis, city officials can forecast the effects of population shifts or new building projects. The visualization of this data enhances transparency with local communities, enabling participatory planning and more equitable outcomes.
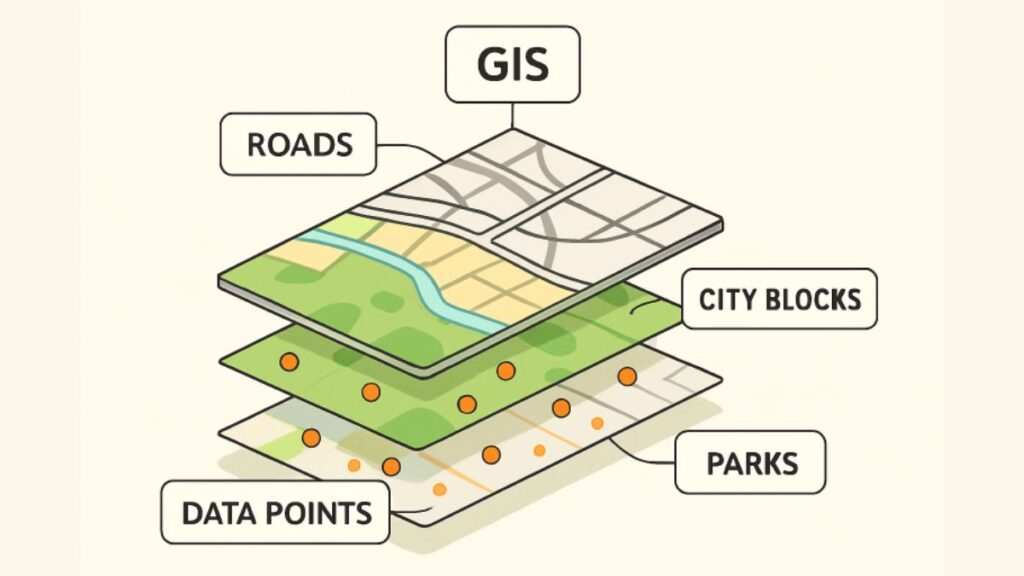
Environmental Management
Environmental management organizations rely on GIS to track habitat changes, manage water resources, and plan conservation efforts. Satellite imagery and remote sensing, integrated through GIS platforms, offer up-to-date snapshots of forest cover, wetlands, and pollution levels. Decision-makers can prioritize conservation initiatives, monitor the outcome of restoration projects, and respond swiftly to threats such as wildfires or invasive species.
In climate action, GIS enables the identification and mitigation of high-risk areas using historical and predictive data. Agencies use these insights to direct funding and resources to communities most vulnerable to extreme weather or dwindling natural resources, making GIS a linchpin of environmental stewardship and sustainability goals.
Healthcare and Public Health
Healthcare professionals leverage GIS to unravel complex patterns of disease transmission, optimize clinic placement, and streamline the allocation of health resources. During outbreaks, GIS mapping supports real-time tracking of infection hotspots and the rapid deployment of intervention measures.
Beyond infectious disease, GIS integrates social determinants of health, such as access to clean water or proximity to pharmacies, helping agencies design more equitable healthcare systems. Nonprofits and community organizations make use of GIS to identify food deserts, target outreach programs, and deliver crucial services to underserved populations.
Transportation and Logistics
GIS mapping streamlines transportation planning by decoding complex traffic flows, identifying congestion patterns, and optimizing delivery routes. Logistics providers incorporate spatial analysis into supply chain decisions, enabling real-time route adjustments for maximum efficiency. This leads to cost savings, reduced emissions, and faster delivery times across industries, from retail to emergency medical supply chains.
Transit agencies and urban mobility planners also turn to GIS to enhance commuter experience, improve public safety, and prioritize infrastructure upgrades. Integration with live sensors and mobile applications gives both planners and travelers unprecedented insight into real-time transit conditions, further reinforcing the value of GIS in an increasingly connected world.
Public Safety and Emergency Response
GIS underpins modern emergency management strategies by mapping risk zones, supporting the planning of evacuation routes, and coordinating multi-agency disaster responses. Law enforcement utilizes spatial analytics to pinpoint crime hotspots and deploy officers proactively, while fire and rescue services use it to plan coverage and allocate resources where they are needed most.
During natural disasters, dynamic hazard mapping and real-time updates enable faster, more effective interventions. GIS also supports community preparedness outreach, ensuring that vulnerable populations are included in early warning and evacuation planning and that resources are available throughout crises.
Agriculture and Natural Resources
Agricultural operations harness GIS for precision farming, land suitability analysis, and crop health monitoring. By layering soil, moisture, and yield data, farmers can fine-tune irrigation and fertilization plans, improving productivity and conserving inputs. Fisheries and forestry professionals use GIS to monitor habitats and manage sustainable harvests, helping balance economic needs with ecosystem preservation.
Predictive modeling with GIS also empowers producers to respond quickly to environmental changes, such as drought or pest outbreaks, ensuring that food production remains resilient amid climate instability.
Advancements in GIS Technology
GIS is rapidly evolving through the integration of artificial intelligence and real-time analytics. These advancements enhance pattern detection, automate feature extraction from satellite images, and enable predictive modeling unmatched by traditional approaches. Cloud-based GIS and mobile mapping have democratized access, allowing field crews and remote workers to collect and update spatial data on the go.
A notable innovation is the application of machine learning, which speeds up big data analysis, enables complex simulations, and assists users in extracting more meaningful insights from intricate datasets. As these tools advance, the potential and influence of GIS will expand, leading to new uses across both established and emerging sectors.
Conclusion
GIS mapping stands at the forefront of industry transformation, providing leaders with critical spatial intelligence to drive innovation, sustainability, and social impact. As GIS capabilities expand—especially with advancements in cloud computing, AI, and real-time monitoring—their integration will be essential in addressing the pressing challenges of urbanization, resource management, and disaster resilience worldwide.