Tribupneu is a term gaining attention in niche technical and consumer circles because it represents a blend of mechanical reliability and modern convenience. Whether you encounter tribupneu as part of industrial equipment, a vehicle component, or a specialized tool, understanding its function, advantages, and care needs will help you make smarter choices. This article explains tribupneu in straightforward language, covers how it works, compares common types, and gives practical maintenance and troubleshooting advice so you can apply the knowledge immediately.
What is tribupneu?
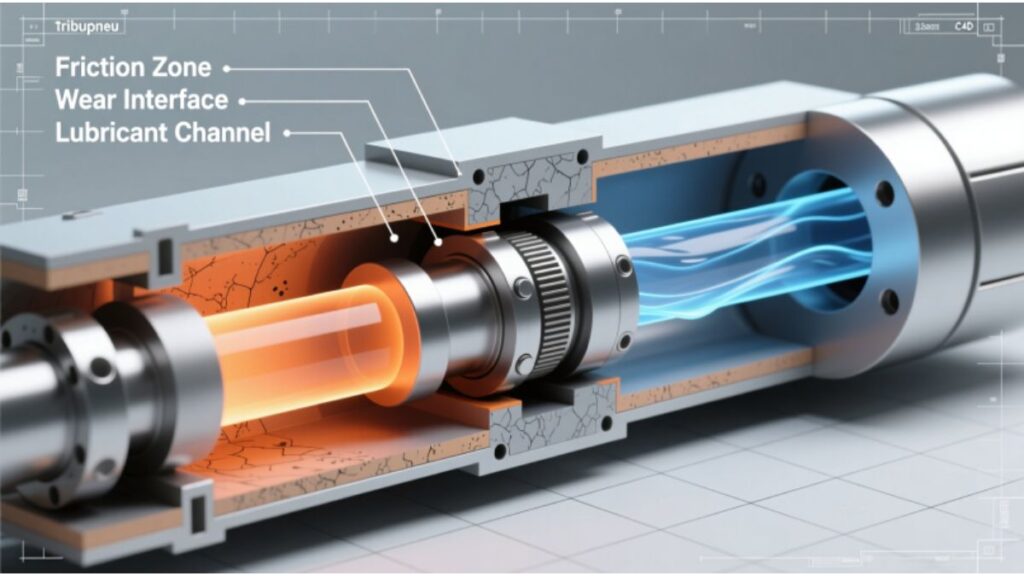
Tribupneu refers to a class of components and systems that combine tribological principles with pneumatic design. In simple words, tribupneu involves managing friction, wear, and lubrication within systems that use compressed air or gas to operate. The name itself is a contraction that hints at tribology and pneumatics working together. A tribupneu system is designed to reduce mechanical wear while maintaining efficient air-powered movement, whether in industrial actuators, vehicle suspensions, or precision instruments.
How tribupneu differs from traditional pneumatic or hydraulic systems
Traditional pneumatic systems rely solely on the compression and expansion of air to move parts, while hydraulic systems use incompressible fluid to transmit force. Tribupneu systems add the explicit focus on surface interaction — the microscopic contact between moving parts — and often incorporate special surface treatments, seals, or lubricants optimized for air-driven motion. This means tribupneu devices aim to achieve quieter operation, longer life, and better performance under variable loads compared with basic pneumatic components.
Core components and design principles
A typical tribupneu unit contains a cylinder or chamber, moving pistons or seals, surface treatments or coatings, and lubrication strategies tailored to air environments. The core design principle is to minimize friction where metal or polymer surfaces meet while maintaining an airtight seal and predictable motion. Engineers working with tribupneu solutions think about three linked aspects: material selection, surface finish, and lubrication compatibility with compressed air. Materials often used include engineered polymers, ceramics, and treated alloys chosen for low friction coefficients and resistance to wear.
Material selection affects durability and maintenance intervals. Surface finish can be engineered to trap thin lubricant films that protect contact surfaces without interfering with air seals. Lubrication strategies in tribupneu systems tend to avoid heavy oils that can atomize or gum up; instead, they favor thin, long-lasting films or solid lubricants integrated into surfaces. This combination results in systems that run cleaner and require less frequent service.
Benefits of adopting tribupneu technologies
The primary benefits of tribupneu lie in reduced downtime, improved energy efficiency, lower noise, and extended component life. With friction controlled and wear minimized, devices remain within tolerance for longer, reducing the need for replacements and major overhauls. Energy efficiency improves because less work is lost as heat when friction is low; in air-driven systems this can translate into lower compressor loads and reduced operational costs. Noise reduction is a notable advantage when tribupneu principles are applied to bearings, seals, and sliding surfaces, producing smoother motion that benefits both industrial settings and consumer products.
Beyond performance, tribupneu designs often allow for lighter components because material strength margins can be reduced when friction and wear are controlled. Weight savings matter in transport and robotic applications where every gram affects energy use and responsiveness. Finally, the controlled-lubrication approaches typical of tribupneu reduce contamination risks in sensitive environments such as cleanrooms or food processing plants.
Common applications and real-world examples
Tribupneu systems appear in a variety of settings where reliable, low-maintenance pneumatic motion is needed. In manufacturing, tribupneu-guided actuators move assembly parts precisely while resisting wear, which reduces calibration frequency. Transportation, adaptive pneumatic suspensions that use tribological coatings or embedded solid lubricants improve ride comfort and lower maintenance. In robotics, small air-driven joints benefit from tribupneu strategies to extend life while keeping motion smooth and predictable.
A practical example can be found in packaging lines where repetitive, high-speed motion causes rapid wear. Replacing standard pneumatic cylinders with tribupneu-enhanced cylinders can lead to months of additional service life and fewer stoppages for seal replacement. Another example is medical device manufacturing, where minimal contamination and precise pneumatic actuation are essential; tribupneu approaches help meet cleanliness and accuracy requirements at the same time.
Types and classifications
Tribupneu products can be categorized by the primary technology they use: surface-treated metal systems, polymer-based low-friction systems, and hybrid systems combining coatings with engineered lubricants. Surface-treated metal systems rely on hard, wear-resistant coatings applied to metal surfaces to reduce abrasive wear. Polymer-based systems use self-lubricating materials that inherently reduce friction. Hybrid systems blend both by applying coatings to metal parts while incorporating polymer seals or sliding elements.
Another way to classify tribupneu devices is by application scale. Micro-tribupneu solutions handle small, precise movements in devices like valves or sensors, whereas macro-tribupneu systems manage larger motions in heavy machinery or transportation. Each scale has distinct design priorities: micro systems focus on minimal stiction and precise control whereas macro systems emphasize load-bearing performance and robustness.
Maintenance, inspection, and longevity strategies
Maintaining tribupneu systems requires a slightly different mindset than caring for standard pneumatic hardware. Because tribupneu components are designed to reduce wear and often use specialized surface treatments, maintenance should prioritize cleanliness, proper air quality, and gentle lubrication where appropriate. Compressed air should be filtered and dried to limit moisture and particulate contamination, both of which can undermine surface treatments and shorten life.
Inspection routines should check for changes in motion smoothness, unusual noise, or slight increases in energy consumption, as these often indicate early-stage wear. When lubrication is required, use products specified by the manufacturer; avoid generic oils that can break down surface films or react with seals. Where tribupneu devices use embedded solid lubricants or dry coatings, avoid introducing external lubricants that could interfere with their function.
Life-extension recommendations include maintaining proper operating pressures, avoiding overloading, scheduling cleaning intervals with non-abrasive methods, and replacing seals with OEM parts that match the tribological design. These steps protect the engineered interfaces that define tribupneu performance and help deliver the long service life the technology promises.
Simple troubleshooting guide
If a tribupneu device starts to exhibit decreased performance, begin troubleshooting by assessing air quality, pressure stability, and any recent changes in operating conditions. First, confirm that air filters and dryers are functional and that condensate is not present in lines. Second, listen for abnormal sounds and observe motion for waviness or stick-slip behavior. If the system feels sticky or jerky, that can indicate contamination of sliding surfaces or failure of a thin lubricant film. Third, inspect seals and rods for visible wear, pitting, or discoloration. Finally, consult manufacturer documentation because some tribupneu coatings have specific repair or replacement procedures that differ from standard pneumatic parts.
When immediate replacement is not possible, temporary restoration can sometimes be achieved by carefully cleaning surfaces with manufacturer-approved methods and ensuring dry, clean air supply. Do not apply heavy lubricants as a stopgap measure; they frequently cause more harm by attracting particulates or altering surface chemistry.
Comparative table: tribupneu vs. standard pneumatic systems
| Feature | Tribupneu Systems | Standard Pneumatic Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Friction control | Engineered surfaces and lubricants reduce friction | Relies on basic seals and generic lubrication |
| Maintenance intervals | Longer, with lower scheduled downtime | Shorter, more frequent service needed |
| Noise levels | Typically lower due to smoother motion | Often higher due to more frictional noise |
| Contamination risk | Lower when dry-lubrication methods used | Higher if oils or contaminants present |
| Upfront cost | Can be higher due to specialized materials | Lower initial cost but possibly higher lifecycle cost |
| Suitability for precision | High; used in fine-motion applications | Moderate; better for simple actuation |
This table demonstrates that tribupneu systems may carry greater initial investment but often return value through longer life, cleanliness, and efficiency. The right choice depends on application priorities.
How to choose the right tribupneu product for your needs
Selecting a tribupneu solution begins by defining the operating environment, load profile, required precision, and maintenance preferences. For high-precision, low-load applications, micro-tribupneu components with polymer surfaces and integrated solid lubricants work well. For heavier loads or harsher environments, surface-treated metal systems with robust seals are preferable. Always consider operating temperature range because some materials and coatings perform poorly at extremes. Evaluate supplier support, warranty terms, and availability of compatible spare parts. A thoughtful selection process avoids common mismatches like using delicate micro-systems in abrasive or highly contaminated environments.
Practical care checklist (phrased as a running narrative)
Caring for tribupneu equipment starts with clean air. Replace or service air filters and dryers on schedule and always drain condensate. Keep the external environment free from dust buildup to minimize particulate ingress. Monitor system performance metrics such as pressure consistency and cycle timing to spot deviations early. When servicing, use manufacturer-recommended parts and procedures, and document the work to track trends over time. If a component shows surface damage, prioritize replacement rather than field repair unless explicitly supported, because improper repair can negate the benefits of tribupneu design.
Conclusion: making the most of tribupneu
Tribupneu represents a practical evolution in pneumatic design that emphasizes longevity, cleanliness, and consistent performance. Whether you are specifying motion components for a new project or considering upgrades to reduce downtime, understanding the principles behind tribupneu — material choice, surface engineering, and targeted lubrication — will help you select the right products and maintain them effectively. With proper installation, clean compressed air, and attention to manufacturer guidance, tribupneu systems can deliver quieter operation, lower lifecycle costs, and fewer interruptions, making them a compelling option for modern pneumatic applications.
FAQs about tribupneu
What is tribupneu and why should I care?
Tribupneu is the integration of tribological design with pneumatic systems to reduce wear, lower friction, and improve the reliability of air-driven motion. You should care because these improvements often reduce downtime and operational costs over the long term.
How long do tribupneu components last compared to standard parts?
Lifespan varies by application, but tribupneu components typically last significantly longer under similar conditions because their surfaces and lubrication strategies reduce wear. Proper maintenance extends this advantage.
Can tribupneu systems be retrofitted into existing equipment?
In some cases yes, but compatibility depends on space, mounting, and operating pressure. Retrofitting may require replacing cylinders, seals, or even piping to ensure the tribological design functions as intended.
Are special lubricants required for tribupneu devices?
Often tribupneu systems use specialized thin-film or dry lubrication strategies and may forbid heavy oils. Always follow manufacturer recommendations to avoid damaging surface treatments.
Is tribupneu suitable for outdoor, dusty environments?
It can be, but additional sealing and filtration measures are essential. For very abrasive environments, choose tribupneu products specifically designed for contamination resistance.
Where can I find spare parts and technical support?
The manufacturer or authorized distributors provide the safest source for spare parts and technical guidance. Using non-OEM parts may reduce performance and void warranties.