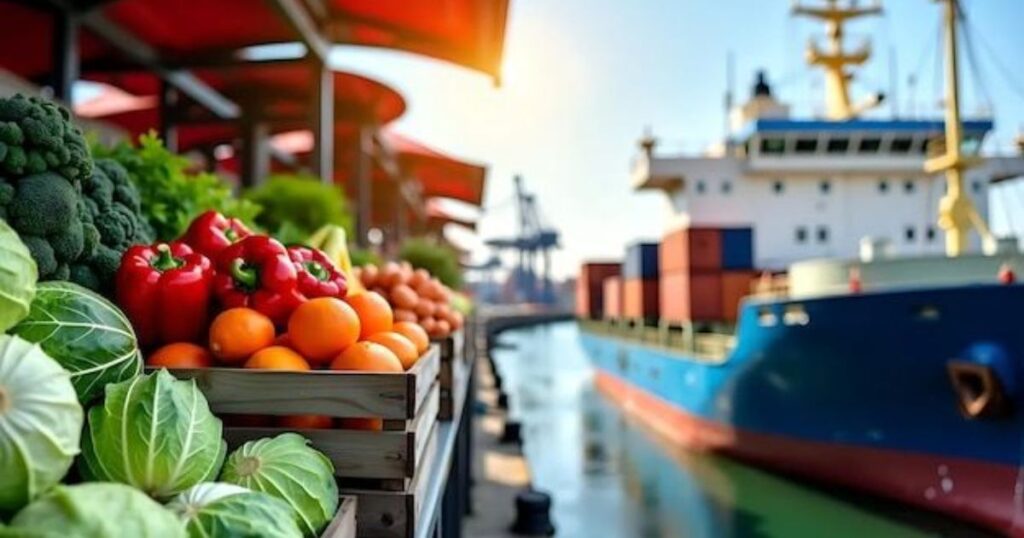
Transporting perishable goods presents unique challenges in today’s global supply chains. Fresh products such as fruits, vegetables, meat, dairy, and seafood require careful handling, temperature control, and timely delivery to maintain quality and safety. For businesses involved in importing, exporting, or distributing perishable items, understanding Perishable Logistics is crucial to prevent spoilage, reduce losses, and ensure customer satisfaction. This guide explains how perishable logistics works, the systems involved, and why many companies rely on Efficient perishable goods logistics and handling processes to streamline their operations.
What Is Perishable Logistics?
Perishable Logistics refers to the specialized management of transporting goods that have a limited shelf life and are sensitive to environmental conditions. Unlike standard freight, perishable products require strict monitoring of temperature, humidity, and handling procedures throughout the supply chain. The objective is to preserve product freshness, maintain food safety standards, and comply with regulatory requirements. Businesses dealing with fresh goods in Australia, particularly in cities like Sydney, Melbourne, and Brisbane, often use Efficient perishable goods logistics and handling processes to ensure their products arrive in optimal condition.
The Importance of Temperature-Controlled Transport
One of the core aspects of Perishable Logistics is temperature control. Cold-chain logistics systems are implemented to maintain a consistent temperature from the point of origin to the final destination. Refrigerated trucks, insulated packaging, and temperature-monitored shipping containers are standard tools used to protect fresh products. Different goods have varying temperature requirements; for instance, fresh seafood requires near-freezing temperatures, whereas tropical fruits may need moderate cooling. By using Efficient perishable goods logistics and handling processes, businesses can prevent temperature fluctuations that cause spoilage or reduce product quality.
Packaging Solutions for Perishable Goods
Proper packaging is another critical component of Perishable Logistics. Packaging not only protects products from physical damage during transport but also helps maintain ideal environmental conditions. Materials such as insulated boxes, gel packs, dry ice, and vacuum-sealed packaging are commonly used. Packaging also assists in tracking and handling, as clearly labelled boxes with temperature-sensitive indicators alert logistics personnel to take special care. Companies that adopt Efficient perishable goods logistics and handling processes often invest in high-quality packaging solutions that reduce waste and extend shelf life.
Key Steps in the Perishable Logistics Process
The journey of perishable goods involves several carefully coordinated steps:
- Collection and Initial Storage: Fresh products are harvested or produced and then quickly moved to temperature-controlled storage facilities to maintain quality. This initial stage is crucial to prevent early spoilage.
- Processing and Sorting: Goods may undergo cleaning, grading, or processing before shipment. Handling practices must minimize exposure to heat, moisture, or contamination.
- Transportation Planning: Selecting the right transport mode—air, road, or refrigerated sea freight—is essential. Perishable goods often require faster delivery, so air freight is common for long distances.
- Cold-Chain Monitoring: Throughout transportation, temperature and humidity are monitored using digital sensors. Deviations can trigger alerts, allowing corrective measures to be taken promptly.
- Customs and Regulatory Compliance: For international shipments, documentation such as health certificates, import/export permits, and food safety compliance records must be submitted. Efficient perishable goods logistics and handling processes ensure all regulations are met.
- Last-Mile Delivery: Timely delivery to retail stores, restaurants, or consumers completes the supply chain. Proper coordination ensures products are delivered in the same condition they left the origin.
Challenges in Perishable Logistics
Managing perishable goods is complex due to several challenges:
- Temperature Sensitivity: Even small temperature fluctuations can spoil goods or reduce their shelf life.
- Transit Delays: Unexpected delays due to traffic, customs inspections, or weather can impact product quality.
- Handling Errors: Improper loading, stacking, or handling can cause physical damage or contamination.
- Regulatory Compliance: International shipments must adhere to strict import/export and food safety laws.
- Limited Shelf Life: Products must reach the end consumer quickly, leaving little room for errors.
Using Efficient perishable goods logistics and handling processes helps businesses mitigate these risks through careful planning, advanced monitoring, and trained personnel.
Technology in Perishable Logistics
Modern Perishable Logistics relies heavily on technology to maintain product quality. Temperature sensors, GPS tracking, and automated alerts allow businesses to monitor shipments in real-time. Data analytics can predict potential delays and optimize delivery routes, while software solutions manage documentation and regulatory compliance. Companies that adopt Efficient perishable goods logistics and handling processes benefit from real-time visibility, reducing the likelihood of spoilage and improving customer satisfaction.
Best Practices for Managing Perishable Logistics
Businesses can enhance their perishable supply chain by implementing the following practices:
- Invest in Refrigerated Transport: Use trucks, containers, and storage units that provide consistent cooling.
- Train Staff Properly: Employees should understand handling, loading, and temperature requirements.
- Select Reliable Partners: Work with logistics providers experienced in Perishable Logistics.
- Monitor Shipments Continuously: Real-time monitoring reduces risks and enables immediate corrective action.
- Use Efficient Packaging: Protect goods physically and maintain appropriate environmental conditions during transit.
- Plan Delivery Routes Strategically: Minimize transit times and reduce exposure to adverse conditions.
Benefits of Efficient Perishable Logistics
Implementing efficient Perishable Logistics offers multiple advantages:
- Reduced Spoilage and Waste: Proper handling and temperature control prevent product loss.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Delivering fresh goods on time improves brand reputation.
- Regulatory Compliance: Meeting food safety and import/export regulations avoids fines or penalties.
- Operational Efficiency: Streamlined processes and reliable partners reduce delays and costs.
- Market Expansion: Efficient logistics enable businesses to distribute products over longer distances safely.
Case Example: Fresh Produce Distribution
Consider a Brisbane-based company exporting fresh fruit to international markets. By implementing Efficient perishable goods logistics and handling processes, the company uses refrigerated containers, monitors shipments in real-time, and partners with customs-compliant forwarders. As a result, the fruit arrives at its destination in peak condition, maintaining quality and freshness. This system demonstrates how effective Perishable Logistics protects products, preserves business reputation, and supports long-term growth.
Conclusion
Perishable Logistics is a vital component of the modern supply chain, especially for businesses dealing with fresh and temperature-sensitive goods. From temperature-controlled transport and specialized packaging to real-time monitoring and regulatory compliance, each step is critical to maintaining product quality. Brisbane businesses, in particular, benefit from partnering with providers who offer Efficient perishable goods logistics and handling processes to streamline operations and reduce risks. By understanding and implementing best practices in Perishable Logistics, companies can minimize spoilage, enhance customer satisfaction, and grow their distribution capabilities.
ALSO READ:Ocean vs. Air Freight: How to Choose the Right Shipping Method