Oral health is often viewed as a separate component of our well-being, but its impact stretches far beyond the mouth. Poor dental hygiene, particularly gum disease, has been linked to a range of health issues, including heart disease. Maintaining healthy gums is crucial not only for your teeth but for your heart as well. In this article, we’ll explore how Oral Health Role in Cardiovascular Health and why it’s essential to care for your gums.
What Is Gum Disease?
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common yet serious condition that affects the gums and bones supporting the teeth. There are two main stages of gum disease: gingivitis and periodontitis.
- Gingivitis is the early stage, characterized by red, swollen gums that may bleed during brushing or flossing. While uncomfortable, it is usually reversible with good oral hygiene.
- Periodontitis is a more advanced form of gum disease. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, where the gums pull away from the teeth, leading to bone loss, loose teeth, and eventually tooth loss.
The primary cause of gum disease is the buildup of plaque—a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth and gums. If plaque isn’t removed through regular brushing and flossing, it hardens into tartar, which further irritates the gums and creates a cycle of inflammation.
Several factors increase the risk of developing gum disease, including poor oral hygiene, smoking, hormonal changes (such as pregnancy), certain medications, and genetics. The symptoms of gum disease often go unnoticed until they become severe, which is why regular dental check-ups are essential. To take proactive steps, visit website to find out more about how oral care can influence your overall well-being.
The Link Between Gum Disease and Heart Disease
The connection between oral health and heart disease has been the subject of numerous studies, and the evidence is clear: gum disease can increase your risk of developing cardiovascular issues. While the exact mechanisms are still being researched, there are several ways in which poor Oral Health Role in Cardiovascular Health.
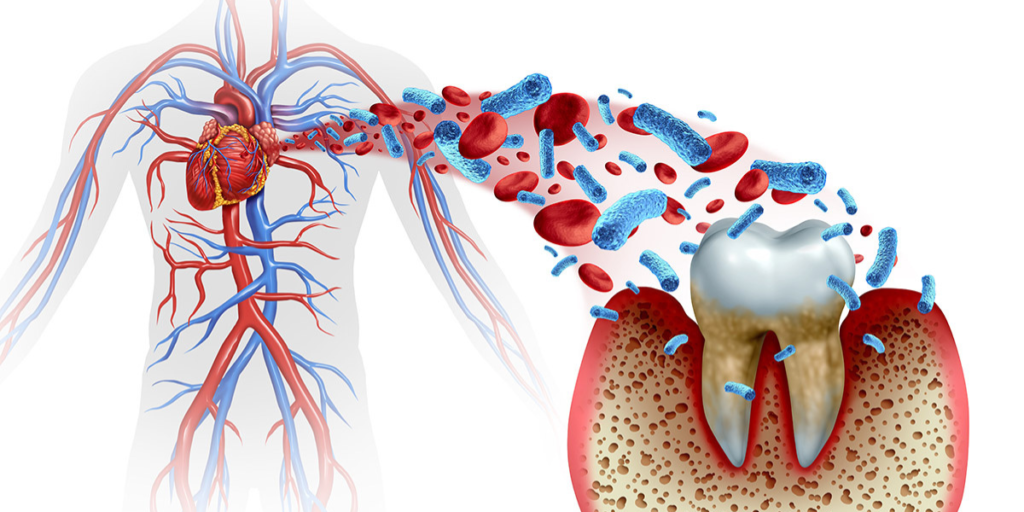
One of the main ways gum disease impacts heart health is through inflammation. When gum disease causes the gums to become inflamed, bacteria from the mouth can enter the bloodstream, triggering an immune response. This constant immune activation can lead to systemic inflammation, which affects not only the gums but also the arteries and blood vessels, contributing to heart disease.
Chronic inflammation is known to play a key role in the development of cardiovascular disease, including atherosclerosis (the hardening of the arteries). When oral bacteria enter the bloodstream, they can contribute to the buildup of fatty deposits (plaque) in the arteries, increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes. Research supports this connection, showing that people with periodontal disease are more likely to develop heart disease compared to those with healthy gums. If you’re interested in the studies behind this, read more about the link between oral health and heart disease.
Pathways Linking Oral Health Role in Cardiovascular Health
Understanding the pathways through which gum disease can influence heart disease helps highlight the seriousness of the issue. There are three main ways this connection works:
1. Bacterial Spread
The bacteria that cause gum disease don’t just stay in the mouth. They can enter the bloodstream through inflamed or damaged gum tissue. Once in the bloodstream, these bacteria can travel to other parts of the body, including the heart, where they may attach to the walls of blood vessels. This can lead to inflammation of the vessel walls and contribute to the formation of atherosclerotic plaque.
2. Inflammation
The body’s immune response to gum disease involves releasing inflammatory molecules to fight off the bacteria. While this is a natural defense mechanism, chronic inflammation can have a damaging effect on the cardiovascular system. Persistent inflammation can narrow the arteries, leading to conditions such as high blood pressure, heart attack, or stroke.
3. Immune Response
Gum disease creates a chronic state of immune activation. This constant immune response can lead to artery damage or contribute to the formation of blood clots, which can block the flow of blood to the heart or brain. Blood clots, in turn, raise the risk of a heart attack or stroke.
Moreover, conditions like diabetes can worsen both gum disease and heart disease, as high blood sugar levels can increase the likelihood of infection and inflammation in the gums, exacerbating the risks for cardiovascular health.
Who’s Most at Risk?
While anyone can develop gum disease, some people are at a higher risk of both gum disease and heart disease. This includes:
- Smokers: Smoking weakens the immune system and makes it harder to fight off infections, including gum disease. It also directly contributes to heart disease by damaging the blood vessels.
- People with diabetes: Diabetic individuals are more susceptible to infections, including gum disease, and they are also at an increased risk for cardiovascular disease.
- Older adults: As we age, our immune system weakens, making it more difficult to combat infections like gum disease, while also increasing the risk of heart disease.
- Those with a family history: Genetics can play a role in predisposition to both gum disease and heart disease.
Certain lifestyle factors such as poor diet, lack of exercise, and high levels of stress also increase the risk for both conditions.
Preventing Gum Disease to Protect Your Heart
Fortunately, there are many ways to prevent gum disease and, by extension, reduce your risk of heart disease. By adopting proper oral hygiene practices and making healthy lifestyle choices, you can protect both your teeth and your heart.
1. Oral Hygiene Tips
- Brush twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and use a soft-bristled brush.
- Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles from between your teeth.
- Regular dental check-ups: Schedule cleanings and exams with your dentist at least twice a year to catch gum disease early.
2. Lifestyle Changes
- Quit smoking: Smoking is one of the most significant risk factors for gum disease and heart disease.
- Maintain a balanced diet: Eating foods rich in vitamins and minerals, such as fruits and vegetables, can help support healthy gums and heart.
- Manage stress: Chronic stress can negatively impact both your oral and heart health.
3. Regular Health Screenings
- Monitor your blood pressure, cholesterol, and glucose levels to catch any early signs of heart disease.
- Discuss oral health: Make sure to mention any gum disease symptoms to both your dentist and doctor to ensure a comprehensive approach to your health.
Conclusion
Gum disease isn’t just a dental problem; it can have serious implications for your heart health. By keeping your gums healthy, you can help protect your heart from cardiovascular disease. Prioritizing oral hygiene, making healthier lifestyle choices, and working with healthcare professionals are crucial steps to lower your risks. Regular dental care and heart health check-ups are intertwined in maintaining overall well-being, so don’t neglect one for the other.