Introduction: Understanding Why Joints Stiff
Feeling your joints stiff after waking up or following long periods of inactivity can be both frustrating and concerning. This common complaint affects people of all ages, especially as we age or lead sedentary lifestyles. Whether it’s your knees, hips, fingers, or shoulders, joint stiffness can impact mobility and overall quality of life.
This article dives deep into why joints get stiff, the key triggers, signs to watch out for, treatment options, and long-term solutions. We’ll explore lifestyle changes, medical interventions, and prevention tips, while integrating key LSI and NLP keywords like joint mobility, joint pain, range of motion, and inflammation. Let’s get started on the path to moving freely again.
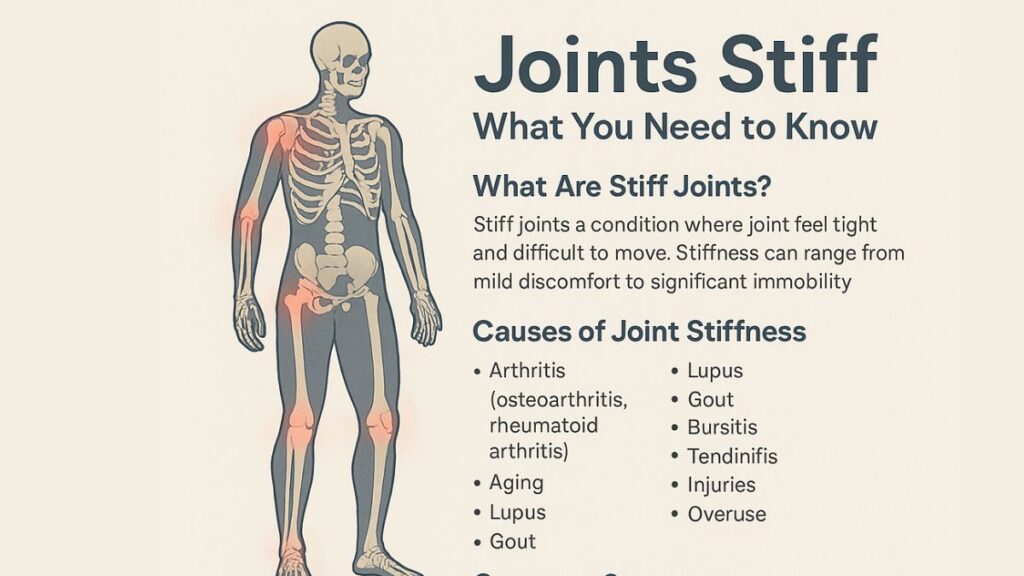
What Does It Mean When Your Joints Stiff Up?
Joints stiff is a phrase that often indicates a decrease in the flexibility or ease of movement in your joints. This can stem from inflammation, injury, or underlying chronic conditions.
When you experience joint stiffness, it may present as:
-
Reduced range of motion
-
Pain when moving
-
Swelling around the joint
-
A sensation of tightness or resistance
While some stiffness can resolve on its own, persistent symptoms might point to issues like arthritis, bursitis, or even joint degeneration.
Top Causes Behind Joints Stiff
1. Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis
Two major culprits behind stiff joints are osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. These conditions cause cartilage breakdown or autoimmune inflammation, reducing lubrication in the joint and increasing stiffness.
2. Aging and Wear-and-Tear
As you age, your synovial fluid, which lubricates joints, may decrease. Coupled with cartilage thinning, this leads to the joints stiff and more painful over time.
3. Injuries or Overuse
An injury from sports, work, or exercise can make joints stiff due to swelling, scar tissue, or instability in the area.
4. Sedentary Lifestyle
Sitting for long periods can reduce joint flexibility, causing them to stiffen. Lack of movement results in reduced circulation and fluid distribution.
5. Gout and Lupus
These inflammatory autoimmune diseases can trigger sudden joint stiffness, especially in the fingers, knees, and feet.
Have you found this topic useful? For more informative content, check out the rest of our blog!
Signs Your Joints Are Stiff for Medical Reasons
-
Morning stiffness lasting over 30 minutes
-
Joints appear swollen or red
-
Stiffness paired with fatigue or fever
-
Sharp pain during basic movement
-
Popping or grinding sounds (crepitus)
Early identification and intervention are key in managing conditions like joint inflammation, autoimmune disease, or ligament damage.
Comparison Chart: Stiff Joints Due to Arthritis vs. Injury
| Characteristics | Arthritis | Injury |
|---|---|---|
| Onset | Gradual | Sudden |
| Duration | Chronic | Temporary (with treatment) |
| Swelling | Often present | May occur with bruising |
| Pain Type | Dull, aching | Sharp, localized |
| Mobility | Decreases over time | Improves as injury heals |
| Morning Stiffness | Common, especially in RA | Rare unless joint immobilized |
| Common Joints Affected | Hands, knees, hips, spine | Depends on injury location |
Effective Treatments for Stiff Joints
When joints stiff up, various treatments can reduce discomfort and restore mobility. Some of the best options include:
1. Physical Therapy and Movement
Targeted range-of-motion exercises, stretching, and low-impact workouts like swimming help reduce stiffness and increase joint fluid movement.
2. Medications
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, and pain relievers manage inflammation and swelling effectively.
3. Heat and Cold Therapy
Using hot packs boosts circulation, while cold compresses reduce inflammation in inflamed or swollen joints.
4. Supplements
Supplements like glucosamine, chondroitin, and omega-3 fatty acids may support joint health and reduce stiffness over time.
5. Weight Management
Excess weight increases pressure on load-bearing joints like the knees and hips, making joints stiff and painful. Maintaining a healthy BMI can prevent further damage.
6. Assistive Devices
Braces, splints, or canes can offload pressure from a stiff joint and provide support during healing or flare-ups.
Daily Habits to Prevent Joints Stiff
Stay Active
Regular movement is the best way to keep joints lubricated and prevent them from stiffening. Include flexibility exercises like yoga or tai chi.
Hydrate Well
Water is essential for joint lubrication. Dehydration may contribute to cartilage damage and joint stiffness.
Anti-Inflammatory Diet
Eating a diet rich in omega-3s, leafy greens, berries, and nuts can lower systemic inflammation and reduce how often joints stiffen.
Posture Matters
Maintaining good posture during work or sleep minimizes stress on joints, especially in the spine, neck, and hips.
Stretch Before and After Activity
Prepping joints before exercise and cooling down after can prevent injuries and reduce muscle tension that affects joint flexibility.
When to See a Doctor About Stiff Joints
You should consult a doctor if:
-
Joints stiff for several days without relief
-
You notice joint deformities or limited range of motion
-
Pain prevents you from daily activities
-
Symptoms worsen with time instead of improving
Long-Term Solutions: Lifestyle, Surgery, or More?
For chronic conditions like arthritis, managing stiffness often requires a long-term care plan.
Lifestyle Changes
Combining physical activity with diet and sleep adjustments goes a long way in reducing how frequently joints stiffen.
Surgical Options
In severe cases of joint degeneration, surgical procedures like joint replacement, arthroscopy, or fusion surgery may be considered.
Injections
Corticosteroid or hyaluronic acid injections provide temporary relief from stiffness and swelling, particularly in knees and shoulders.
Best Exercises to Improve Stiff Joints
-
Swimming: Low-impact and promotes joint movement without pressure.
-
Walking: Keeps knees, hips, and ankles active.
-
Stretching: Daily full-body stretching improves mobility.
-
Resistance Bands: Builds strength in supporting muscles.
-
Yoga: Increases flexibility, balance, and reduces tension in joints.
How Nutrition Impacts Joint Health
Eating anti-inflammatory foods can reduce flare-ups and chronic stiffness.
Recommended foods:
-
Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel)
-
Leafy greens (spinach, kale)
-
Fruits (blueberries, oranges)
-
Whole grains
-
Nuts and seeds
Avoid processed foods, excess sugar, and red meats that may promote inflammation and make your joints stiff.
Start of Conclusion: Why You Shouldn’t Ignore Joints Stiff
Ignoring the signs when your joints stiff can result in long-term damage, limited mobility, and reduced quality of life. Taking early action through lifestyle adjustments, proper diagnosis, and treatment can preserve joint function and improve comfort.
Understanding the root cause—whether from aging, injury, or a medical condition—will guide the most effective intervention. With consistent care, you can reduce the frequency and severity of joint stiffness and return to a more active life.
FAQs About Stiff Joints
1. Are stiff joints always a sign of arthritis?
No, while arthritis is a common cause, joint stiffness can also result from injuries, overuse, or inactivity.
2. What’s the best exercise for relieving stiff joints?
Low-impact activities like swimming, stretching, and walking help improve flexibility and reduce stiffness.
3. Can diet affect joint stiffness?
Yes, anti-inflammatory foods can reduce joint pain and swelling, improving mobility.
4. When should I see a doctor about my joints stiff?
If stiffness lasts several days, worsens, or affects daily life, it’s time to consult a healthcare professional.
5. How can I prevent joints from getting stiff as I age?
Staying active, eating well, maintaining good posture, and stretching regularly can help.
6. Is it normal to feel stiff in the morning?
Mild morning stiffness is common, but if it lasts over 30 minutes or worsens, it may signal an underlying issue.