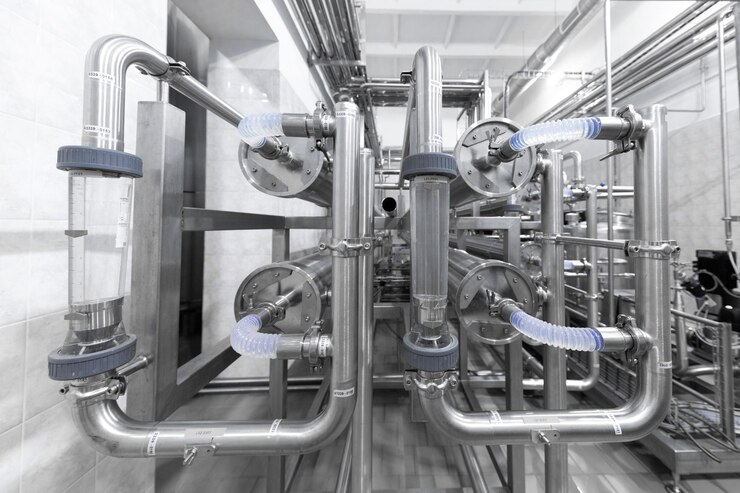
What is Retube?
Introduction to Retube
Ever heard of retubing? It’s not just another buzzword; it’s a game-changer. Retube is the process of replacing or refurbishing the tubes in devices like boilers, heat exchangers, and condensers. It’s a crucial technique used across various industries to maintain and enhance the efficiency and lifespan of these systems. Imagine the tubes as the veins of a machine—without healthy veins, the whole system can falter.
Importance and Relevance in Today’s World
In today’s fast-paced and environmentally conscious world, retubing has become more relevant than ever. Industries are under constant pressure to be more efficient, reduce downtime, and operate sustainably. Retubing meets these demands by ensuring systems run smoothly and last longer, thereby saving costs and reducing environmental impact.
History and Evolution of Retube
Origins of Retube
The concept of retubing dates back to the early industrial revolution. As machinery and steam engines became integral to production, maintaining these machines became a priority. Engineers realized that replacing the worn-out tubes could rejuvenate the entire system, leading to the birth of retubing.
Key Milestones in Retube’s Development
Over the decades, retubing has evolved with technological advancements. From manual replacement methods to automated and precise techniques, the journey has been remarkable. Notable milestones include the introduction of automated tube cleaning and inspection tools, which have significantly increased the efficiency and accuracy of the retubing process.
How Retube Works
Basic Mechanisms
At its core, retubing involves removing old, degraded tubes and replacing them with new ones. This can be done in several ways, depending on the machinery and the industry’s requirements.
Core Components
Key components involved in the retubing process include the tubes themselves, tube sheets, and the tools for removal and installation. High-quality materials and precision engineering are essential for ensuring the new tubes fit perfectly and perform optimally.
Technological Framework
Modern retubing leverages advanced technologies like robotics and AI for inspection and replacement. These technologies allow for more precise measurements and a more efficient replacement process, minimizing human error and maximizing productivity.
Applications of Retube
Industrial Uses
Retubing is widely used in industries like power generation, petrochemicals, and manufacturing. Boilers and heat exchangers in these industries undergo regular retubing to maintain efficiency and safety.
Medical Applications
In the medical field, retubing is crucial for devices like sterilizers and certain diagnostic equipment. Ensuring these devices operate without fail is critical for patient safety and effective medical treatment.
Environmental Impact
Retubing also plays a significant role in reducing environmental impact. By extending the life of machinery and improving efficiency, it helps in reducing waste and lowering energy consumption.
Benefits of Retube
Efficiency and Productivity
One of the primary benefits of retubing is the significant boost in efficiency and productivity. New tubes ensure better heat transfer, leading to improved performance of the entire system.
Cost-Effectiveness
Retubing is a cost-effective alternative to replacing entire systems. It allows industries to maintain their equipment without the hefty expense of new installations.
Sustainability
By extending the lifespan of equipment, retubing promotes sustainability. It reduces the need for new materials and decreases the environmental footprint of manufacturing new components.
Challenges and Limitations
Technical Barriers
Despite its benefits, retubing comes with technical challenges. The process requires skilled technicians and precise tools, which can be a barrier for some industries.
Market Adoption
While retubing is widely recognized in some sectors, others are slower to adopt these techniques due to a lack of awareness or perceived complexity.
Regulatory Hurdles
Regulations around equipment maintenance and replacement can also pose challenges. Navigating these regulations requires expertise and can slow down the adoption process.
Future Prospects of Retube
Innovations and Trends
The future of retubing looks bright, with continuous innovations enhancing the process. From improved materials to more sophisticated robotic systems, the industry is set to become even more efficient and effective.
Potential Market Expansion
As more industries recognize the benefits of retubing, the market is likely to expand. Emerging markets and sectors will increasingly adopt these techniques, driving growth and development.
Long-term Impact
In the long run, retubing will play a crucial role in sustainable industrial practices. By maintaining and enhancing existing systems, it supports a more resource-efficient and environmentally friendly approach to industrial maintenance.
Case Studies
Successful Implementations
Many industries have successfully implemented retubing with impressive results. For instance, a major power plant reported a 20% increase in efficiency after retubing its boilers.
Lessons Learned
These case studies highlight the importance of skilled technicians and proper planning. They also demonstrate the significant benefits that can be achieved with careful implementation.
How to Get Started with Retube
Initial Steps
Starting with retubing involves assessing your current equipment and identifying the need for retubing. Regular inspections can help determine when retubing is necessary.
Resources and Tools
There are numerous resources and tools available for those looking to start retubing. From online tutorials to professional services, finding the right support is crucial.
Best Practices
Following best practices such as regular maintenance schedules and using high-quality materials can ensure the success of your retubing efforts.
Common Misconceptions About Retube
Myths vs. Reality
One common misconception is that retubing is too costly and complex. In reality, it is a cost-effective and manageable process that offers significant benefits.
Clarifying Doubts
Educating stakeholders about the real benefits and processes of retubing can help overcome these misconceptions and encourage adoption.
Comparing Retube with Other Technologies
Advantages Over Traditional Methods
Compared to traditional methods of replacing entire systems, retubing is far more economical and efficient. It minimizes downtime and maximizes resource use.
Limitations Compared to Emerging Technologies
While retubing offers many benefits, it does have limitations when compared to some emerging technologies that might offer more advanced solutions but at a higher cost.
Community and Support for Retube Users
Online Communities
Joining online communities and forums can provide valuable insights and support from other retubing professionals.
Professional Networks
Building a professional network with experts in the field can also offer significant advantages, from knowledge sharing to partnership opportunities.
Support Resources
There are numerous support resources available, including technical guides, workshops, and customer service from retubing equipment providers.
Tips for Maximizing Retube’s Potential
Optimization Techniques
Using optimization techniques such as predictive maintenance can help maximize the benefits of retubing. Predictive maintenance involves monitoring equipment for signs of wear and tear and addressing issues before they lead to significant problems. This proactive approach ensures that the retubing process is timely and effective.
Maintenance Tips
Regular maintenance is key to extending the lifespan of retubed equipment. Implementing a maintenance schedule that includes regular inspections, cleaning, and minor repairs can prevent major issues down the line. It’s like taking your car in for regular oil changes to avoid engine failure.
Advanced Strategies
For those looking to get the most out of their retubing efforts, advanced strategies such as using high-efficiency tube materials and incorporating smart technology can be beneficial. Smart sensors and IoT (Internet of Things) devices can provide real-time data on tube performance, allowing for more precise and timely maintenance.
Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
Retubing is a vital process that enhances the performance, efficiency, and longevity of various industrial and medical equipment. By understanding the importance, applications, and benefits of retubing, industries can make informed decisions to maintain their systems effectively.
Final Thoughts
As technology continues to advance, retubing techniques will become even more sophisticated, offering greater efficiency and sustainability. Embracing these advancements will be key to staying competitive in a fast-evolving industrial landscape.
(FAQs)
What is retubing?
Retubing is the process of replacing or refurbishing the tubes in machinery like boilers and heat exchangers to improve efficiency and extend the equipment’s lifespan.
Why is retubing important?
Retubing is crucial for maintaining the efficiency, safety, and longevity of industrial equipment. It helps in reducing downtime and operational costs while promoting sustainability.
How often should retubing be done?
The frequency of retubing depends on the type of equipment and its usage. Regular inspections can help determine the right timing, but typically, retubing may be needed every 5-10 years.
What materials are used for new tubes?
Common materials include stainless steel, copper alloys, and titanium, chosen for their durability and resistance to corrosion and heat.
What are common signs that retubing is needed?
Decreased efficiency, leaks, and visible corrosion or damage to the tubes are common signs that retubing is necessary.
Can retubing be done while the equipment is operational?
Retubing usually requires the equipment to be shut down to ensure safety and accuracy in the replacement process.