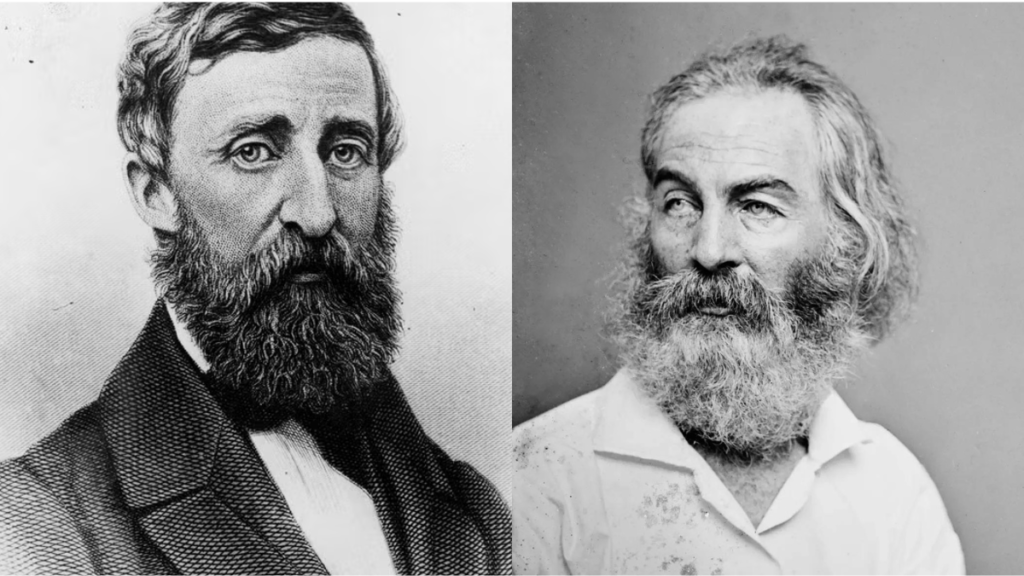
The literary landscape of 19th-century America was profoundly shaped by two iconic figures: Walt Whitman and Henry David Thoreau. While their works and philosophies differed in many respects, exploring the influence of Walt Whitman on Thoreau reveals intriguing intersections between their ideas. This article delves into how Whitman’s innovative approach to literature and his philosophical outlook impacted Thoreau, highlighting their complex relationship and the broader implications for American transcendentalism.
Walt Whitman and Henry David Thoreau: A Brief Overview
Before examining the influence of Whitman on Thoreau, it’s essential to understand their respective contributions to American literature and thought. Walt Whitman, celebrated for his groundbreaking poetry collection Leaves of Grass, is known for his use of free verse and his celebration of the individual and the American experience. His work is characterized by its expansive form, inclusiveness, and a deep reverence for nature and humanity.
Henry David Thoreau, on the other hand, is renowned for his philosophical reflections on nature and society, encapsulated in works such as Walden and Civil Disobedience. Thoreau’s writings focus on the value of simple living, the importance of personal integrity, and the need for social reform. While Thoreau’s prose is more structured compared to Whitman’s free verse, both writers explore themes of nature, individualism, and societal critique.
Shared Philosophical Foundations
Walt Whitman and Henry David Thoreau were both influenced by the transcendentalist movement, which emphasized the inherent goodness of people and nature and the importance of individual intuition. Whitman’s expansive view of the self as part of a larger, interconnected whole resonates with transcendentalist beliefs. His poetry celebrates the individual’s connection to nature and the universe, reflecting a profound sense of unity and inclusiveness.
Thoreau’s engagement with transcendentalist ideas is evident in his writings, particularly in Walden, where he explores the self’s relationship with nature and society. Thoreau’s philosophy of living deliberately and his reflections on nature echo Whitman’s themes of individualism and spiritual connection to the natural world. The mutual philosophical ground they share highlights the influence of Whitman’s ideas on Thoreau’s work.
Literary Styles and Techniques
One of the most notable ways Whitman influenced Thoreau was through his innovative literary style. Whitman’s use of free verse and his departure from traditional poetic forms represented a radical shift in American literature. His poems often employ repetition, parallelism, and an expansive, almost conversational tone that was groundbreaking for its time.
Thoreau, though primarily a prose writer, was undoubtedly aware of Whitman’s poetic experimentation. The lyrical quality of Thoreau’s prose, particularly in Walden, reflects a response to Whitman’s influence. Thoreau’s writing incorporates vivid imagery and philosophical reflection, creating a style that, while more structured than Whitman’s poetry, shows a nuanced engagement with similar themes and techniques.
Thematic Resonances
Themes of nature, individualism, and social critique are central to both Whitman and Thoreau’s works, illustrating the profound impact of Whitman on Thoreau. Whitman’s celebration of nature as a source of inspiration and spiritual renewal finds a parallel in Thoreau’s detailed observations and reflections in Walden. Thoreau’s portrayal of nature as a nurturing and enlightening presence mirrors Whitman’s depiction of the natural world as a vital, life-affirming force.
Additionally, both writers explore the theme of individualism, though in different ways. Whitman’s poetry extols the virtues of the individual and the importance of personal expression, while Thoreau’s writings emphasize the value of self-reliance and personal integrity. The resonance of these themes in Thoreau’s work reflects Whitman’s influence and highlights their shared philosophical concerns.
Political and Social Views
Both Whitman and Thoreau were vocal about their political and social views, though their approaches differed significantly. Whitman’s work often reflects a democratic ideal and a belief in the potential for social and political transformation through personal and collective enlightenment. His poetry celebrates democracy and the American spirit, advocating for a more inclusive and egalitarian society.
Thoreau’s Civil Disobedience presents a more direct critique of social and political institutions, arguing for individual resistance against unjust laws. While Thoreau’s activism was focused on specific issues such as slavery and the Mexican-American War. Whitman’s broader vision of social harmony and democratic ideals likely reinforced Thoreau’s commitment to social justice and reform.
Impact on Thoreau’s Later Works
The influence of Whitman on Thoreau is evident in Thoreau’s later writings, which reflect a deeper engagement with the themes of individualism and nature. Thoreau’s essays and reflections become more profound and introspective, showcasing an integration of Whitman’s ideas into his own philosophical framework.
In addition to thematic influences, Thoreau’s prose adopts a more lyrical quality in response to Whitman’s poetic innovations. The evolution of Thoreau’s writing reveals an appreciation for the stylistic and thematic possibilities introduced by Whitman, highlighting the impact of Whitman’s work on Thoreau’s literary development.
Conclusion
The influence of Walt Whitman on Henry David Thoreau underscores the rich interplay between two of America’s most influential literary figures. While their styles and philosophies diverged in many respects, Whitman’s impact on Thoreau is evident in their shared thematic concerns, literary experimentation, and philosophical reflections. Whitman’s celebration of the self, nature, and democracy found a resonant echo in Thoreau’s writings. Highlighting the interconnectedness of their intellectual and creative endeavors.
Thoreau’s engagement with Whitman’s ideas enriched his own work, leading to a deeper exploration of nature, individualism, and social justice. This relationship highlights the enduring influence of Whitman on Thoreau and the broader context of American transcendentalism.
FAQs
How did Walt Whitman’s poetry influence Henry David Thoreau’s writing style?
Whitman’s use of free verse and his innovative approach to poetry had a notable impact on Thoreau’s writing style. Although Thoreau wrote prose, his work, particularly in Walden, reflects a lyrical quality and vivid imagery similar to Whitman’s poetry. Thoreau’s prose exhibits a rhythmic and contemplative nature influenced by Whitman’s poetic experimentation.
What were the shared philosophical views of Whitman and Thoreau?
Both Whitman and Thoreau were influenced by transcendentalism. Which emphasized the inherent goodness of people and nature, and the importance of self-reliance and individual intuition. Their works reflect a deep appreciation for nature, individualism, and social critique, though they approached these themes from different perspectives.
How did Thoreau’s views on nature reflect Whitman’s influence?
Thoreau’s reflections on nature in Walden demonstrate a profound reverence for the natural world, akin to Whitman’s portrayal of nature in Leaves of Grass. Thoreau’s detailed observations and philosophical musings reflect a deep engagement with themes similar to those explored by Whitman, showcasing the influence of Whitman’s work on Thoreau.
Did Whitman and Thoreau have a personal relationship or correspondence?
There is no extensive record of personal correspondence between Whitman and Thoreau. However, their works suggest a significant intellectual exchange. Both were part of similar literary and philosophical circles, and their writings reflect a mutual influence despite their differing approaches.
How did Whitman’s democratic ideals influence Thoreau’s political views?
Whitman’s democratic ideals and belief in social transformation likely reinforced Thoreau’s commitment to social justice and individual responsibility. While Thoreau’s activism focused on specific issues, Whitman’s broader vision of social harmony. And democratic values likely influenced Thoreau’s approach to social critique and reform.