In 2024, the number of reported robberies in the United States decreased by 13.6% compared to 2023. This is based on the FBI’s Quarterly Uniform Crime Report, which compares data from agencies that voluntarily submitted data for the first six months of 2023 and 2024.
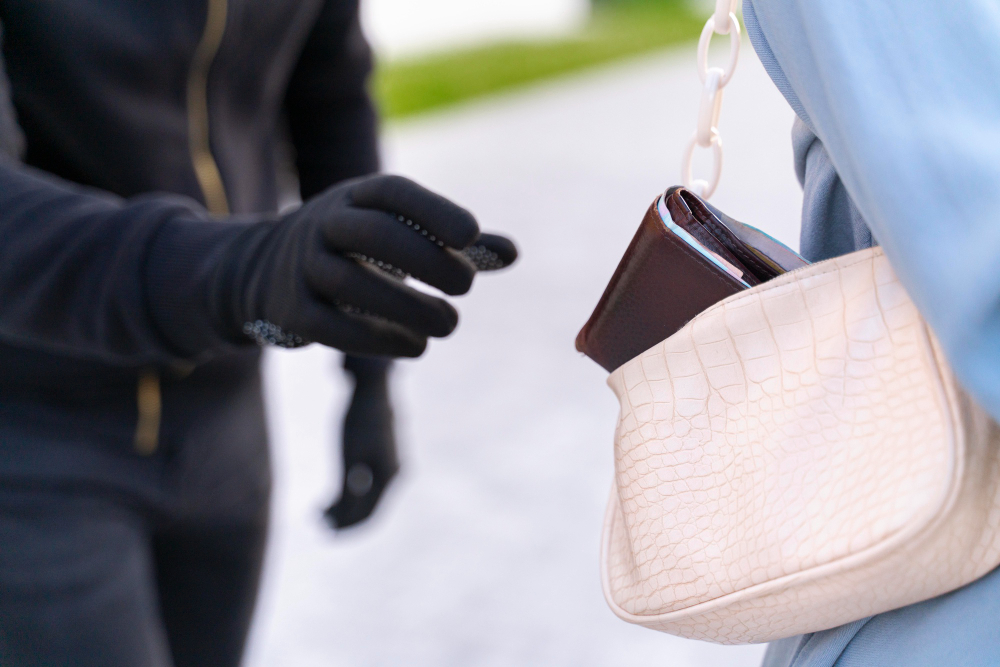
Aggravated robbery means a serious and complex crime that involves the use of force, threats, or intimidation to steal property from another person. This crime involves aggravating circumstances that make it more severe compared to larceny or petty theft since it makes the victim more vulnerable to harm.
This article will talk about the different factors surrounding an aggravated robbery case and how you can defend yourself against it.
Understanding Aggravated Robbery
Aggravated robbery occurs when someone points a gun in your face and demands your personal belongings.
If you are charged with an aggravated robbery, you can file a demurrer, especially if the prosecution has not provided enough evidence to support the charge of aggravated robbery.
Is a demurrer a motion? A demurrer is indeed a type of motion and it is a formal request to the court to dismiss or modify the charges. If a demurrer is granted, a defendant cannot be guilty of aggravated robbery even if all the complaint allegations are true.
Key Elements of Aggravated Robbery
The act of taking property, the use of force or intimidation, the intent to gain, and the lack of consent are all key components for a crime to be classified as aggravated robbery.
The victim’s impression of risk is very important. If a victim feels more threatened during the incident, the more serious the offense becomes.
The presence of accomplices is another aggravating circumstance.
These factors then combine to ultimately form a more serious charge that would result in serious penalties upon conviction.
Legal Consequences of Aggravated Robbery
Individuals convicted of aggravated robbery can suffer various penalties depending on the state where the crime was committed.
A usual prison sentence for aggravated robbery’s goes from 5 to 25 years or even longer. The length of imprisonment is determined by local state laws, the severity of the crime, and the alleged offender’s possible prior criminal record.
Fines could also go into six-digit territory, usually numbering tens of thousands of dollars and above. A conviction would most likely result in a permanent criminal record. Which could limit your ability to find work and have other consequences for your life.
Prevention and Awareness Strategies
Awareness programs and preventive strategies can help individuals and communities deal with aggravated robbery’s.
Familiarize yourself with crime trends in the area and always be aware of your surroundings.
Be observant and avoid distractions, especially when in an unfamiliar area.
Start or join neighborhood watch groups to promote vigilance and safety in your community. Your community must maintain open communication with local law enforcement, which is a great source of information and potential support.
Install security features like surveillance cameras and alarm systems in your home and store. Don’t hesitate to report any suspicious activities that you may have observed.
Enroll in self-defense training courses and encourage others to do the same. These proactive measures can help mitigate the chances of aggravated robbery’s.