In the realm of geometry and mechanical design, analogies can often help us understand complex concepts by drawing parallels between familiar objects and ideas. One such analogy is: bicycle wheel : circle :: ___ : radius nyt. This article explores this analogy to shed light on the relationship between bicycle wheels and circles, and how the concept of radius fits into this comparison.
Understanding the Analogy
Bicycle Wheel and Circle
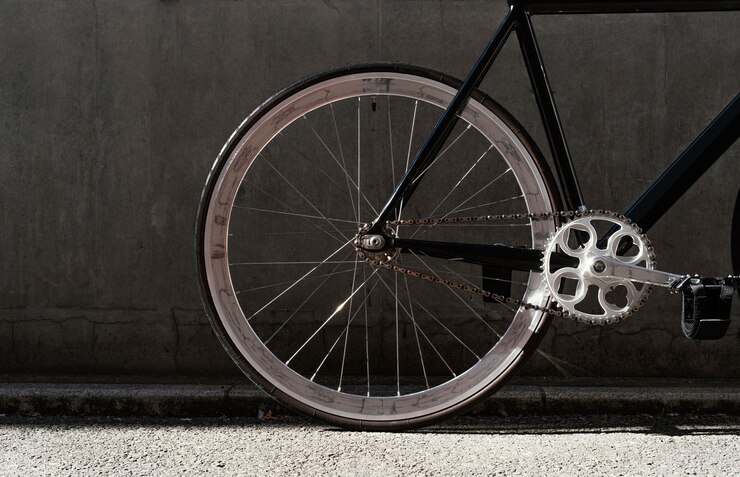
A bicycle wheel is fundamentally a circle. It shares the same geometric properties, such as having a center point and a circumference determined by its radius. In this analogy, the bicycle wheel represents the circle, which is a shape defined by its radius and circumference.
The Missing Element
To complete the analogy bicycle wheel : circle :: ___ : radius nyt, we need to identify the counterpart to radius in the context of a bicycle wheel. The key here is to recognize what element or concept in the context of a bicycle wheel corresponds to the radius in the context of a circle.
The Role of Radius in Bicycle Wheels
Defining Radius
The radius of a circle is the distance from the center to any point on the circumference. For bicycle wheels, the radius is crucial as it determines several aspects of the wheel’s performance and characteristics:
- Wheel Size: The radius of a bicycle wheel determines its size, which directly affects the bike’s handling, comfort, and speed. Larger wheels have a greater radius and circumference, while smaller wheels have a smaller radius.
- Performance Metrics: The radius affects how far the bicycle travels with each wheel revolution. A larger radius means a larger circumference, which translates to covering more distance per revolution.
The Counterpart to Radius
In the context of a bicycle wheel, the counterpart to the radius is the diameter. The diameter of a bicycle wheel is twice the radius, representing the full width of the wheel from one edge to the other, passing through the center.
Diameter vs. Radius in Bicycle Wheels
Calculating Diameter
The diameter (D) of a bicycle wheel can be calculated from the radius (r) using the formula:
D=2rD = 2rD=2r
Understanding this relationship helps in various practical applications:
- Gear Ratios: The diameter of the wheel influences the bike’s gear ratios and how efficiently power is transferred from the pedals to the wheel.
- Speed and Distance: The diameter, along with the radius, affects the bike’s speed and the distance traveled per revolution. This is essential for cyclists who are keen on tracking their performance.
Choosing the Right Diameter
Selecting the appropriate diameter for a bicycle wheel depends on the type of biking you plan to do:
- Road Bikes: Typically use wheels with a diameter of 700c (approximately 622 mm), providing a balance of speed and efficiency on paved surfaces.
- Mountain Bikes: Often use 26-inch or 27.5-inch wheels, which offer better control and stability on rough terrains.
- Hybrid Bikes: May use a range of diameters, balancing characteristics from both road and mountain bikes.
Practical Applications and Considerations
Impact on Bike Handling
The diameter of the wheel impacts how a bike handles different surfaces. Larger wheels provide a smoother ride and better rollover capability, while smaller wheels offer more agility and quicker acceleration.
Effect on Comfort
A larger diameter wheel can help absorb shocks and bumps more effectively, leading to a more comfortable ride, especially on uneven surfaces.
Maintenance and Adjustments
Maintaining the correct diameter and ensuring proper tire pressure is crucial for optimal performance. Regular checks and adjustments can prevent issues related to handling and efficiency.
Conclusion
In the analogy bicycle wheel : circle :: ___ : radius nyt, the missing element that completes the comparison is the diameter. Understanding the relationship between radius and diameter is essential for grasping the geometric principles behind bicycle wheels and their performance. By exploring these concepts, cyclists can make informed decisions about their equipment and enhance their riding experience.
FAQs
How does the diameter of a bicycle wheel affect its performance?
The diameter affects the wheel’s speed, handling, and comfort. Larger diameters cover more distance per revolution and provide a smoother ride, while smaller diameters are more responsive and agile.
What is the relationship between diameter and radius?
The diameter is twice the radius. For a bicycle wheel, this means that knowing the diameter allows you to calculate the radius and vice versa.
Why is it important to choose the right wheel diameter for your bike?
Choosing the correct diameter ensures optimal performance and comfort. It impacts factors such as handling, speed, and stability, making it crucial for different types of biking.
How can I determine the best wheel diameter for my riding needs?
Consider your riding style and terrain. Road bikes typically use larger diameters for speed, while mountain bikes use smaller diameters for control and stability.
What maintenance should I perform on my bicycle wheels?
Regular maintenance includes checking for damage, ensuring proper tire pressure, and inspecting the wheel for proper truing to ensure smooth and efficient performance.